We all know the first four letters of HTTP when typing an internet address. This changes and goes to a more secure environment, adding the letter "s" and becoming https. Using "s" in http illustrates the use of a security protocol on the Web site, known as SSL.
We all know the first four letters of HTTP when typing an internet address. This changes and goes to a more secure environment, adding the letter "s" and becoming https. Using "s" in http illustrates the use of a security protocol on the Web site, known as SSL. What does that mean? It means there is encryption at the point between the server and the end user's browser. From January 2017, all browsers will inform the user with indications in the address line (url) where they use their codes or make payments if their details are safe or not. Below we will see some changes that will happen to two known browsers.
Chrome
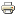
Chrome plans to alert users to an unsafe website that requests codes or payments with the phrase "Not Secure". As shown in the figure below.
 Firefox
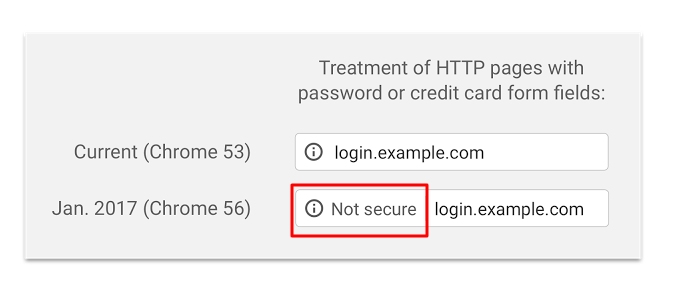
FirefoxFirefox will move in the same logic as Chrome where it will show a lock with a red line as shown in the picture below.
 Not available features
Not available featuresSeveral features of Chrome, such as geolocation, device motion / orientation, etc., will only be available in https.
Fast http protocolThe http / 2.0 protocol (which will soon be available on shared hosting services of innoview.gr) is replacing the http protocol, which makes it faster. This is supported through https in Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, Safari, and Opera. Websites that have gone to http / 2.0 should have SSL.
No owner would like to have a red mark indicating that his site is not safe. Create a secure environment for your website and visitors with the innoview.gr SSL certificates
See the SSL certificates provided by innoview.gr